Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shiba, Tsuyoshi*; Kamezaki, Hiroshi*; Yuyama, Tomonori*; *
JNC TJ9400 2000-012, 92 Pages, 2000/02
This research aims to develop a system in which aspects necessary for FBR cycle and overall comparison of evaluation items (economy, safety etc.) are evaluated quantitatively and objectively as a part of Nuclear Cycle development's research project of the FBR cycle for practical use. There are various methods in the decision-making support. In this particular situation, features of each method were evaluated based on the analysis of cases with each method. Subsequently we constructed overall evaluation method by combining Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), Multi-attribution Utility Function Method (MUF) and Cut-off Method. This method has variation in evaluation items, transparency in evaluation process and uncompensation. The six aspects of evaluation are economy, effectiveness of resource use, proliferation resistance, environmental effectiveness, safety, and research and development. The evaluation items and the evaluation index of each aspect were hierarchized and the evaluation structure was constructed. In the present study effect function for each evaluation index and pair comparison for examining significance of each item were utilized to select prospective systems for FBR cycle experimentally. The result confirmed reliability of our general assessment system as a decision-making support system for FBR system.
PNC TN9410 98-059, 53 Pages, 1998/06
The analysis program code STEDFAST; Space, TErrestrial and Deep sea FAST reactor ・gas turbine system; had been developed in PNC to get the best values of system parameters on fast reactor ・gas turbine power generation systems used as power sources for deep sea, space and terrestrial cogeneration. In this report, we performed a parameter survey analysis by using the code to study characteristics of the systems. Concerning the deep sea fast reactor ・gas turbine system, calculations with many variable parameters were performed on the base case of a NaK cooled reactor of 40kWe. We aimed at total equipment weight and surface area necessary to remove heat from the system as important values of the characteristics of the system Electric generation power and the material of a pressure hull were specially influential for the weight. The electric generation power, reactor outlet/inlet temperatures, a natural convection heat transfer coefficient of sea water were specially influential for the area. Concerning the space reactor ・gas turbine system, the calculations with the variable parameters of compressor inlet temperature, reactor outlet/inlet temperatures and turbine inlet pressure were perfomed on the base case of a Na cooled reactor of 40kWe. The first and the second variable parameters were influential for the total equipment weight of the important characteristic of the system. Concening the terrestrial fast reactor ・gas tubine system, the calculations with the variable parameters of heat transferred pipe number in a heat exchanger to produce hot water of 100  C for cogeneration, compressor stage number and the kind of primary coolant material were performed on the base case of a Pb cooled reactor of 100MWt. In the comparison of calculational results for Pb and Na of primary coolant material, The primary coolant weight flow rate was naturally large for the fomer case compared with for the latter case because density is very different between them. ...
C for cogeneration, compressor stage number and the kind of primary coolant material were performed on the base case of a Pb cooled reactor of 100MWt. In the comparison of calculational results for Pb and Na of primary coolant material, The primary coolant weight flow rate was naturally large for the fomer case compared with for the latter case because density is very different between them. ...
PNC TN9410 98-044, 47 Pages, 1998/06
Thermal striping phenomena characterized by stationary random temperature fluctuations are observed in the region immediately above the core exit of liquid-metal-cooled fast breeder reactors (LMFBRs) due to the interactions of cold sodium flowing out of a control rod (C/R) assembly and hot sodium flowing out of adjacent fuel assemblies (F/As). Therefore the in-vessel components located in the core outlet region, such as upper core structure (UCS), flow guide tube, C/R upper guide tube, etc., must be protected against the stationary random thermal process which might induce high-cycle fatigue. In this study, thermal striping conditions at the tee junction in the MONJU EVST system (maximum temperature difference : 110  C, Velocity ratio between main and branch pipes : 0.25) were investigated numerically by the use of computer programs. From the investigations, the following results have been obtained: (1) Effects of the secondaly flows generated by the existence of 90
C, Velocity ratio between main and branch pipes : 0.25) were investigated numerically by the use of computer programs. From the investigations, the following results have been obtained: (1) Effects of the secondaly flows generated by the existence of 90 elbow located at upstream position of the tee junction were negligeble, because the flow velocity in the main pipe is 0.25 of the flow velocity in the branch pipe. (2) A ration between maximum and effective amplitudes of the temperature fluctuations calculated by the DINUS-3 code was 3.18. It was concluded that the value 6.0 as the ratio used in the integrity evaluation of the EVST system is a coservative side. (3) There was a limit in ability of a time-averaged multi-dimensional code AQUA, in the evaluation of thermal striping phenomena with recirculation flows. One of the reasons was considered that the local equilibrium of turbulence flows was not established in this tee junction problem.
elbow located at upstream position of the tee junction were negligeble, because the flow velocity in the main pipe is 0.25 of the flow velocity in the branch pipe. (2) A ration between maximum and effective amplitudes of the temperature fluctuations calculated by the DINUS-3 code was 3.18. It was concluded that the value 6.0 as the ratio used in the integrity evaluation of the EVST system is a coservative side. (3) There was a limit in ability of a time-averaged multi-dimensional code AQUA, in the evaluation of thermal striping phenomena with recirculation flows. One of the reasons was considered that the local equilibrium of turbulence flows was not established in this tee junction problem.
; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki
PNC TN9410 98-069, 128 Pages, 1998/05
There is a growing tendency to need structural analysis aided expert system, which adopts advanced analysis techniques and is useful adaptive design of large reactor. This report describes about development of the h-version adaptive mesh division function based on Yuge & Iwai method. From points of view about securing of analysis precision, reduction of work to make analysis data and decrease in calculation costs, to analyze smoothly the nonlinear problems is the main object of this system. The h-version adaptive mesh technique is the method that increases locally finite element mesh density, depending on dividing the elements that the absorbed energy quantity exceeds a standard value every increment step. We developed this h-version adaptive mesh division function and incorporate it in the general nonlinear finite element code. For the function this system has, we show the following. (1)It is possible to apply this system to the thermos elastic-plastic nonlinear problem. (2)The provided finite elements (a)4-Node Quadrilateral Plane-Stress Element (b)4-Node Quadrilateral P1ane-Strain Element (c)4-Node Quadrilateral Axisymmetric Solid Element (d)4-Node Layered Shell Element (3)The provided constitutive model (a)Ono-model (b)kinetic hardening rule (c)ORNL 10 cycles hardening rule (4)The repetition technique : Newton-Raphson technique (5)The application possible force type (a)The concentrated forces (b)The distributed forces (c)The self forces (d)The temperature forces (6)It is possible to apply the cyclic repetition force. (7)The dividing the elements technique (a)Rectifying the strain of the element shape depending on the aspect ratio (b)Dividing the elements that the absorbed energy quantity exceeds a standard value every increment step. (c)Add the function of input the plural absorbed energy quantity that is the estimate value of the division elements. The programming and giving the tests about this system was put into by RCCM.
; Moro, Satoshi; ; Kakehi, Isao; ;
PNC TN9410 98-033, 284 Pages, 1998/03
System engineering division of OEC has being carried out a design study of the advanced nuclear fuel recycle system using electro-metallurgical process, aiming for improvements in safety, reliability, economy and a1so in environmental burden and nuclear non-proliferation. But the public criticism against nuclear power is more severe recently, and the situation is changing as seeing in the conclusion of the round-table conference on FBR. The researcher's meetings, in which researchers in PNC and from other organizations attended, were held during December, 1997 and March, 1998 in order to discuss on the advanced nuclear fuel recycle system and technology for FBR to be aimed in the future, and how to execute its research & development, etc. The conclusions of this meeting are as follows: (1)The future advanced FBR fuel cycle system shall be the system which has high potential for maximum utilization of uranium resources, and also for revolutionary improvements of economy, safety, environmental burden, etc. so as to be accepted in the society. (2)Regarding to the process of the future fuel eycle system, electro-metallurgical process that is able to apply for reprocessing of different types of fuel (oxide, metal and nitride) and is flexible for technical progress is recommended. Research & development of this system and technology shall be carried out. (3)The mission of PNC (new organization) is to select the most appropriate advanced FBR fuel cycle system from the viewpoint of the long-term FBR age in the future, and to conduct development of its system. It is expected for the new organization to execute its research and development steadily in cooperation with other research institutes, etc. under the nation-wide assessment and agreement. According to the above conclusions, the system engineering division will enhance the design study of the advanced FBR fuel cycle system and establish the definite concept of the system in cooperation with concerned in and ...
; ; ; Ando, Hideki
PNC TN9410 97-094, 27 Pages, 1997/10
The 11th periodic inspection had been executed at the experimental fast reactor JOYO from May 10,1995 to March 24,1997. Because the inspection had been extended several times, the time span of external exposure control was divided into two period. The result of collective dose equivalent in the previous term(from May 10,1995 to December 7,1996: about seventeen months) was 243.34 man*mSv, whereas, the expected collective dose equivalent was about 280man*mSv. The result of collective dose equivalent in the latter term (from December 8,1996 to March 24,1997: about three months) was 44.73 man*mSv, whereas, the expected collective dose equivalent was about 85man*mSv. The collective dose equivalent in the whole period of this inspection was 288.07 man*mSv. It was confirmed that this inspection was carried out with the suitable radiation protection programmes. In this report, the method for the control of external exposure and the reduction of external exposure, provided in 11th periodic inspection, were described with taking the results of the past periodic inspections into consideration.
Maruyama, Tadashi; ; ; Onose, Shoji;
PNC TN9410 97-077, 177 Pages, 1997/07
Postirradiation examinations of JOYO MK-II control rods have been carried out since 1983, where 16 subassemblies with total 110 absorber pins of initial load to the fifth reload control rods have been subjected to a number of both non-destructive and destructive examinations. In the course of postirradiation examinations, a cracking of cladding tube was found in the total 15 absorber pins in five control assemblies. This paper indicates the results of postirradiation examinations and analysis of absorber pin performance using CORAL code to elucidate the cause of absorber pin cracking in JOYO MK-II control rods. No crack was found in absorber pins whose maximum burnup was lower than 39  10
10 cap/m
cap/m , whereas all the cracked pins had burnup of higher than 43
, whereas all the cracked pins had burnup of higher than 43  10
10 cap/m
cap/m with the initial gap between B
with the initial gap between B C pellet and cladding larger than 0.44 mm. The cracks were found at around positions corresponding to the lowest B
C pellet and cladding larger than 0.44 mm. The cracks were found at around positions corresponding to the lowest B C pellet in the stack. The ceramography analysis indicated that B
C pellet in the stack. The ceramography analysis indicated that B C pellet exhibited extensive cracking and a part of gap between pellet and cladding closed. The cladding deformation had an ovality and the cracks tended to occur at the shorter diameter side. The cracked surface of absorber pin was of a typical grain boundary fracture. The result of He analysis for the cladding material indicated a substantial amount of He accumulation at the inner surface of cladding, but the bulk He content was not anomalously high compared with those in the neutron irradiated stainless steels. TEM observation indicated He bubbles was not clearly found in the as-irradiated cladding material. The cause of cladding failure was attributed to the ACMI where the gap closure due to relocation of B
C pellet exhibited extensive cracking and a part of gap between pellet and cladding closed. The cladding deformation had an ovality and the cracks tended to occur at the shorter diameter side. The cracked surface of absorber pin was of a typical grain boundary fracture. The result of He analysis for the cladding material indicated a substantial amount of He accumulation at the inner surface of cladding, but the bulk He content was not anomalously high compared with those in the neutron irradiated stainless steels. TEM observation indicated He bubbles was not clearly found in the as-irradiated cladding material. The cause of cladding failure was attributed to the ACMI where the gap closure due to relocation of B C pellet took place from early times of irradiation. The code analysis by CORAL indicated that the cladding strain due to ACMI was not fully absorbed by the irradiation creep and that the plastic strain became large enough to ...
C pellet took place from early times of irradiation. The code analysis by CORAL indicated that the cladding strain due to ACMI was not fully absorbed by the irradiation creep and that the plastic strain became large enough to ...
Aoto, Kazumi; ; ; ; ; Hirakawa, Yasushi
PNC TN9420 97-007, 786 Pages, 1997/06
The results of the research on the damaged thermocouple well which caused the sodium leak accident at the outlet of the C-loop intermidiate heat exchanger (IHX) of the secondary heat transfer system of the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju are described in this report. A lot of tests, inspections, observations and measurements were carried out to confirm that the thermocouple well and its attachments to the pipe including welded part are normal by checking the possibility of weld failure or corrosion at the clearance which may cause the damage of the thermocouple well, and to get information of the dimensions relating the estimation of the leaked sodium volume and the leakage path, etc. These tests, etc., were performed for the thermocouple well except the fractured surface, the thermocouple well, the welded parts between the thermocouple well and the attachment, and between the attachment and the outlet pipe, etc., as written below. (1)Accurate measurement of the dimension. (2)Inspection to check the fixing condition between the thermocouple well and the attachment. (3)Measurement of the residual stress. (4)Non destructive testing at some points. (5)Chemical composition analysis. (6)Microscopic observation of metalogical structure at the welded part. (7)Hardness test. (8)Research on corrosion at the clearance. (9)Structure strength test of the thermocouple well. (10)Bending test of the thermocouple's sheath at high temperature.
; ; Tanabe, Hiromi; Ohno, Shuji; Miyake, Osamu;
PNC TN9410 97-030, 93 Pages, 1997/04
A sodium fire analysis code, ASSCOPS(Analysis of Simultaneous Sodium Combustions in Pool and Spray) was developed coupling the computer codes of SPRAY-IIIM and SOFIRE-MIl to assess temperature-pressure transients resulting from sodium spray and pool combustions, simultaneously. The validation of ASSCOPS was conducted using the experimental results obtained from sodium spray fire experiments using 21 m vessel and the accuracy of calculated results was discussed. The following results were obtained: (1)Study under inert gas atmosphere. The comparison between analysis and experiment with regard to the pressure and the temperature showed a good agreement. (2)Study under air atmosphere. The comparison between analysis and experiment with regard to the pressure and the temperature also showed a good agreement. (3)Effects of parameter used in evaluating the design of Monju. The peak pressure and temperature obtained by the analysis overestimates the experimental results. From these results, it was concluded that the development and validation of ASSCOPS indicate a improvement on the burning and the heat transfer models in SPRAY-IIIM.
vessel and the accuracy of calculated results was discussed. The following results were obtained: (1)Study under inert gas atmosphere. The comparison between analysis and experiment with regard to the pressure and the temperature showed a good agreement. (2)Study under air atmosphere. The comparison between analysis and experiment with regard to the pressure and the temperature also showed a good agreement. (3)Effects of parameter used in evaluating the design of Monju. The peak pressure and temperature obtained by the analysis overestimates the experimental results. From these results, it was concluded that the development and validation of ASSCOPS indicate a improvement on the burning and the heat transfer models in SPRAY-IIIM.
*
PNC TJ9607 97-001, 64 Pages, 1997/03
When minor actinides (MA) are returned to a core of fast breeder reactor for tbe purpose of incineration of them, rare earth nuclides and so on (RE) are also returned to the core because the separation of MA from RE is difficult at present. Then, accurate neutron cross section data of RE become necessary for investigating the characteristics of the core. Therefore, the measurement of keV-neutron capture cross sections of 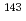 Nd and
Nd and 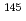 Nd were performed to obtain tbe accurate data. The measurement was relative to the standard capture cross sections of
Nd were performed to obtain tbe accurate data. The measurement was relative to the standard capture cross sections of  Au. A neutron time-of-flight method was adopted witb a ns-pulsed neutron source by a Pelletron accelerator and a large anti-Compton Nal(T1) gamma-ray detector. As a result, the capture cross sections of those nuclides were obtained with the error of about 4 % in an incident neutron energy region of 10 to 560 keV. A comparison between the present data and the evaluated values of JENDL-3.2 showed tbat JENDL-3.2 provided good evaluations for
Au. A neutron time-of-flight method was adopted witb a ns-pulsed neutron source by a Pelletron accelerator and a large anti-Compton Nal(T1) gamma-ray detector. As a result, the capture cross sections of those nuclides were obtained with the error of about 4 % in an incident neutron energy region of 10 to 560 keV. A comparison between the present data and the evaluated values of JENDL-3.2 showed tbat JENDL-3.2 provided good evaluations for 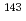 Nd, but underestimated the capture cross sections of
Nd, but underestimated the capture cross sections of 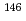 Nd by 10-20 % at neutron energies below 30 keV and overestimated them by about 20 % at 560 keV, whereas it provided good evaluations in the energy region of 40-70 keV. The discrepancy is caused by the weak dependency of evaluated cross sections on the incident neutron energy.
Nd by 10-20 % at neutron energies below 30 keV and overestimated them by about 20 % at 560 keV, whereas it provided good evaluations in the energy region of 40-70 keV. The discrepancy is caused by the weak dependency of evaluated cross sections on the incident neutron energy.
Takeda, Toshikazu*; Unesaki, Hironobu*; Kurisaka, Kenichi*; Sakuma, Hiroomi*; Shimoda, Masayuki*; Ito, Noboru*; Kugo, Teruhiko*; Aoki, Shigeaki*; Uto, Nariaki*; Tanaka, Motonari*
PNC TJ2605 88-001, 230 Pages, 1988/03
no abstracts in English
Higashi, Kunio*; Shin, Kazuo*
PNC TJ2604 87-001, 31 Pages, 1987/03
no abstracts in English
; Yumoto, Ryozo; Sasajima, Hideyoshi*; *
PNC TN841 71-27, 92 Pages, 1971/10
no abstracts in English
Sasa, Toshinobu
no journal, ,
As a part of the activities of the "Research Committee for Thorium Nuclear System" in the Japan Atomic Energy Society, the characteristics, performance and feasibility of the proposed thorium nuclear systems from recently published open documents were surveyed in order to understand the research and development status of the thorium nuclear system around the world. Research has been conducted in the countries using nuclear power in the world such as India, Asia, Europe, and the United States. Pebble fuel or molten salts (thermal and fast neutron systems) are selected as fuel material. Regarding the core thermal output, proposals were selected from several 100 MW for demo reactors and modular reactor to 5 GW for power reactors. For the feasibility point of view, many proposals are still in the concept study phase, but there are a few concepts which aimed at licensing of already approved the domestic environmental impact assessment.